Electrical violations can be both a safety hazard and an expense for homeowners. Understanding the most common electrical problems discovered during home inspections can help prevent accidents and address issues before they become costly repairs.
In this article, we will explore the common electrical violations found during a home inspection, the top 5 most uncovered violations, and how to prevent and address them.
The top 5 most common electrical code violations uncovered in home inspections
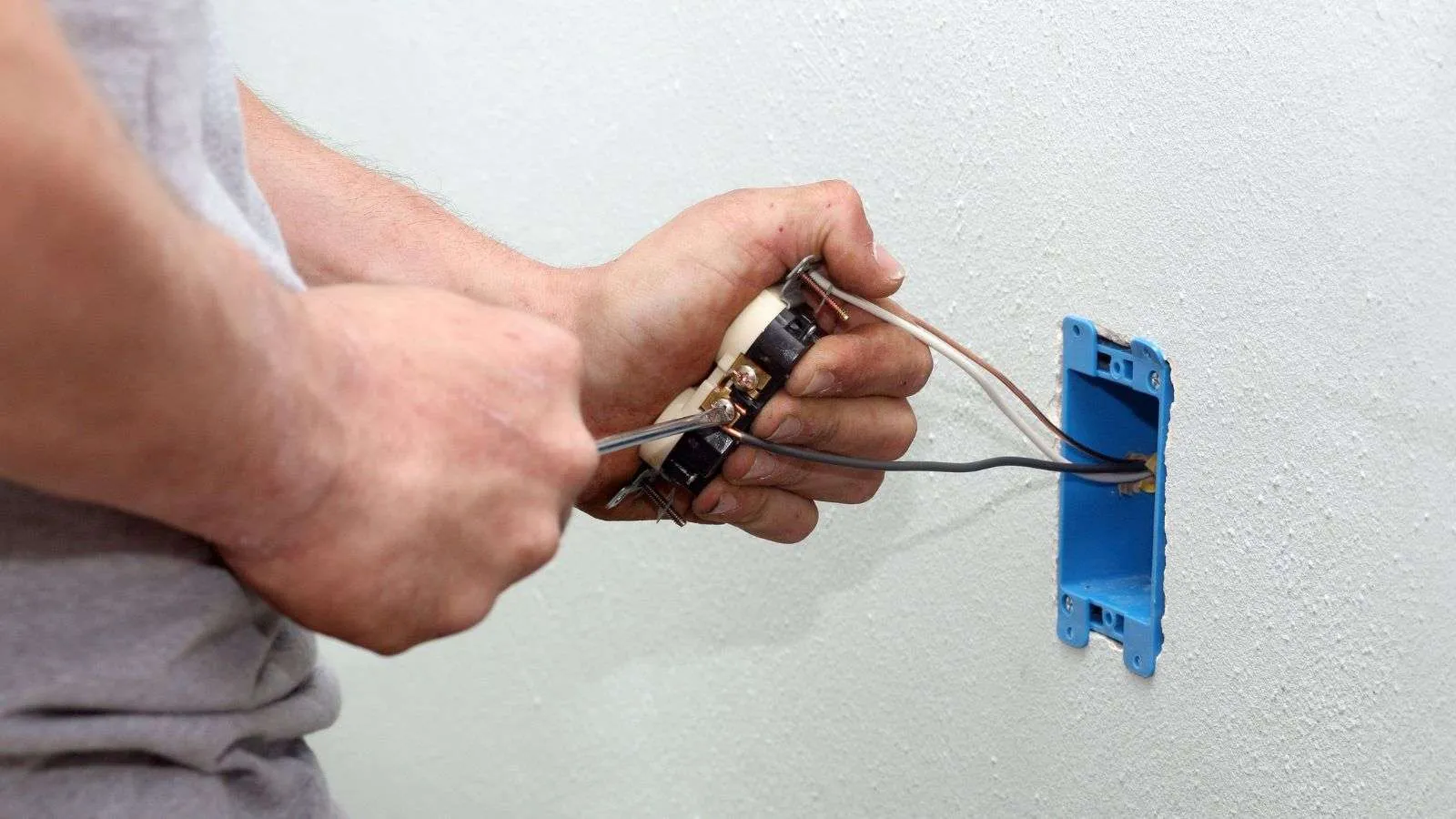
1. Improperly installed electrical outlets
When it comes to electrical outlets, improper installation is a common violation found during home inspections. This can include outlets that are not securely attached to the wall, have loose or exposed wiring, or are not grounded properly. Make sure that outlets are installed by a licensed electrician and meet the required safety standards.
- Use outlet boxes that are large enough to accommodate the wiring and provide ample space for connections.
- Avoid the possibility of electrical outlets becoming loose by anchoring them securely to walls.
- Double-check the polarity of the outlet to make sure the hot and neutral wires are connected correctly.
- Proper grounding is one way to protect yourself from an electrical shock and keep your entire electrical system running smoothly.
2. Inadequate electrical panel clearance
Another common violation discovered in home inspections is inadequate clearance around electrical panels. The National Electrical Code (NEC) sets specific requirements for the space in front of and around electrical panels to maintain safe access and operation. Insufficient clearance can hinder maintenance and create a potential fire hazard.
- Maintain a minimum clearance of 36 inches in front of the electrical panel to allow for easy access during maintenance or emergencies.
- Avoid storing any items in front of or blocking access to the panel, as this can hinder proper operation.
- Make sure that the panel has enough room around it for ventilation to prevent overheating.
- Consider installing a clear and permanent label indicating the purpose of each circuit breaker for easy identification.
3. Inadequate GFCI protection
Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI) protection is important for areas exposed to moisture, such as kitchens, bathrooms, and outdoor outlets. Inadequate GFCI protection is often found in home inspections, putting occupants at risk of electrical shocks.
- Install GFCI outlets in all areas where water is present, including within six feet of sinks, tubs, showers, and outdoor areas.
- Test GFCI outlets monthly to ensure they are functioning properly. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for testing procedures.
- Consider upgrading standard outlets to GFCI outlets in older homes or areas without proper protection.
- Install weather-resistant GFCI outlets in outdoor locations to withstand exposure to the elements.
4. Incorrectly wired switches
Improper wiring of switches is another common electrical code violation that can pose safety risks. Switches should be wired correctly to control the intended lighting or electrical devices. Incorrect wiring can lead to short circuits, overheating, or even electrical fires.
- Familiarize yourself with proper switch wiring diagrams before attempting any electrical work.
- Turn off the power, and then check that it is actually turned off with a voltage tester before working on switches.
- Connect wires securely using appropriate wire connectors or terminal screws.
- Label switch boxes with their corresponding circuit breakers to easily identify and troubleshoot any issues.
5. Overloaded circuits
Overloading electrical circuits by connecting too many devices or appliances is a violation commonly found during home inspections. It can lead to overheating, tripping breakers, and potential fire hazards.
- Distribute electrical devices and appliances across different circuits to evenly distribute the load.
- Be mindful of power-hungry appliances such as air conditioners, heaters, and high-wattage kitchen appliances.
- Consider adding additional circuits or upgrading your electrical panel if you frequently experience tripped breakers or overloaded circuits.
- A licensed electrician can help you assess your electrical needs and make sure that circuits are properly designed and installed.
What role do electrical panels play in home inspection issues?
During a home inspection, the electrical panel is thoroughly examined to make sure it meets safety standards and is functioning properly. Common issues that can arise with electrical panels include inadequate clearance, outdated or damaged components, improper wiring connections, and overloaded circuits.
These issues can pose safety risks such as electrical shocks, fire hazards, and system failures. Inspectors pay close attention to the condition of the electrical panel, its capacity to handle the electrical load, the presence of any code violations, and the overall safety of the wiring connections. Identifying and addressing electrical panel issues is essential for maintaining a safe and reliable electrical system in a home.
How can these electrical violations lead to safety hazards?
- Improperly installed electrical outlets can lead to loose connections, exposed wiring, and potential electrical shocks.
- Inadequate electrical panel clearance can hinder access to the panel during maintenance or emergencies and can also increase the risk of fire hazards.
- Inadequate GFCI protection in areas exposed to moisture can lead to electrical shocks and potential electrocution.
- Incorrectly wired switches can cause short circuits, overheating, and electrical fires.
- Overloaded circuits can result in overheating, tripped breakers, and potential fire hazards.
Why is proper grounding essential for electrical safety?
- Prevention of electrical shocks: Grounding provides a safe path for electrical current to flow in the event of a fault or short circuit, reducing the risk of electrical shocks.
- Protection against electrical fires: Grounding helps prevent electrical fires by providing a low-resistance path for fault currents to flow, minimizing the risk of fire hazards.
- Stabilization of voltage levels: Proper grounding helps stabilize voltage levels, ensuring reliable and safe operation of electrical systems and protecting sensitive electronic devices.
- Equipment safety and longevity: Grounding protects electrical equipment by providing a path for fault currents to dissipate safely, reducing the risk of damage, and extending the lifespan of appliances and electronics.
- Compliance with electrical codes and standards: In electrical codes and standards, grounding is a safety requirement. Proper grounding practices help meet regulations and create a safe environment for occupants.
How do overloaded circuits contribute to electrical violations?
Overloading circuits contributes to electrical violations by placing excessive demand on the electrical system beyond its intended capacity. This can lead to overheating of wires and components, tripped breakers, fire hazards, and violations of electrical codes and standards. Overloading circuits can cause insulation to deteriorate, raising the possibility of electrical fires and system damage.
Tripped breakers act as a safety mechanism to prevent further damage, but frequent tripping indicates an ongoing overload issue. Overloaded circuits also pose fire hazards due to the excess heat and can violate electrical codes that specify maximum load capacities for circuits.
To prevent overloading circuits, you have to distribute electrical loads properly, be mindful of power requirements, and consult with a licensed electrician to address any potential issues.
What are common issues, specifically with electrical outlets, found during inspections?
- Loose or wobbly outlets: Outlets that are not securely attached to the wall can be a safety hazard and may indicate improper installation.
- Exposed wiring: Wiring that is visible or not properly enclosed within the outlet box can pose a risk of electrical shocks and should be addressed.
- Missing or damaged outlet covers: Outlets without covers or with damaged covers may expose live electrical components, increasing the risk of accidents.
- Reverse polarity: This occurs when the hot and neutral wires are connected in reverse, which can lead to potential electrical hazards and cause equipment damage.
- Lack of GFCI protection: In areas exposed to moisture, such as kitchens and bathrooms, the absence of GFCI outlets or improper placement can pose a safety risk.
- Insufficient grounding: Outlets without proper grounding or with faulty grounding can increase the risk of electrical shocks and may not meet safety standards.
- Overloaded outlets: Plugging too many devices into a single outlet can overload the circuit and create a fire hazard.
How often should a homeowner get their electrical system inspected?
Homeowners should consider getting their electrical system inspected at least once every 5 to 10 years, or more frequently if there are specific concerns or issues. Regular inspections of electrical circuits will help identify problems before they occur and prevent an unsafe or inefficient system. Homeowners should schedule an electrical inspection when purchasing a new home or before undertaking major renovations or additions that may require electrical work.
To find a qualified electrical inspector, homeowners can explore directory websites such as Big Home Projects that provide listings and reviews of professionals in their area. These platforms can help homeowners find reputable inspectors who can assess their electrical system thoroughly and provide expert advice and recommendations.
How can improper wiring with switches and fixtures cause problems?
These issues include malfunctioning or non-functional switches, which can be frustrating and inconvenient. Incorrect wiring connections can lead to short circuits and electrical fires, posing significant safety hazards. Faulty wiring also increases the risk of electrical shocks, as individuals may come into contact with live wires.
Dimming or flickering lights are common signs of improper wiring, indicating loose connections or inadequate wire sizing. Moreover, poor wiring practices can put excessive strain on electrical devices, resulting in premature failure and increased maintenance costs.
To avoid these problems, you have to make sure that switches and fixtures are wired correctly by following proper wiring diagrams and techniques.
What are GFCI and AFCI requirements, and how do they impact home inspections?
GFCI and AFCI (Arc Fault Circuit interrupters) are electrical safety devices that have specific requirements and impact home inspections. GFCI outlets are designed to protect against electrical shocks in areas exposed to moisture, such as kitchens, bathrooms, and outdoor outlets. AFCI devices, on the other hand, are designed to detect and prevent electrical arc faults, which can potentially cause electrical fires.
Both GFCI and AFCI requirements are outlined in electrical codes and standards. During a home inspection, inspectors will check for the presence of GFCI outlets in appropriate areas and AFCI protection in required circuits, such as bedrooms and living spaces. If GFCI or AFCI requirements are not met, it can result in code violations and potential safety hazards.
Why is the use of extension cords a concern during a home inspection?
First and foremost, extension cords are not intended to be a permanent solution for electrical power. They are designed for temporary use and can become potential safety hazards when used improperly or for extended periods. Extension cords can easily become overloaded if multiple devices are plugged into them, leading to overheating, tripped breakers, and fire risks.
They can be a trip hazard if not properly secured or placed in high-traffic areas. Home inspectors pay close attention to the use of extension cords during inspections to ensure that they are used appropriately and meet safety standards.
It is generally recommended to avoid excessive reliance on extension cords and instead consider installing additional outlets or seeking the assistance of a licensed electrician to address any electrical power needs in a safer and more permanent manner.
What steps can homeowners take to address and prevent electrical violations?
- Schedule regular electrical inspections: Arrange for periodic inspections by a licensed electrician to identify any potential issues or violations within the electrical system.
- Address code violations promptly. If any electrical code violations are discovered during an inspection, work with a qualified electrician to rectify the issues and bring the system up to code.
- Avoid DIY electrical work. Leave complex electrical tasks to professionals. Attempting DIY electrical work without proper knowledge and expertise can lead to safety hazards and code violations.
- Properly install electrical outlets: Make sure that electrical outlets are installed securely, grounded correctly, and meet the required safety standards. Seek professional help if needed.
- Use GFCI outlets in appropriate areas: Install GFCI outlets in areas exposed to moisture, such as kitchens, bathrooms, and outdoor locations, to prevent electrical shocks.
- Avoid overloading circuits. Distribute electrical loads evenly across multiple circuits to prevent overloading. Be mindful of power-hungry appliances and devices that may strain the electrical system.
- Maintain adequate clearance around electrical panels: Keep at least 36 inches of clearance in front of and around electrical panels to maintain safe access for maintenance and reduce fire risks.
- Replace outdated or damaged wiring: If you have old or damaged wiring, consider updating it to ensure safety and compliance with current electrical codes.
- Test and replace faulty switches or fixtures. Regularly check switches and fixtures for proper functionality. Replace any that are malfunctioning, damaged, or outdated.
- Educate yourself on electrical safety: Stay informed about electrical safety practices, such as how to properly use extension cords, avoid overloading outlets, and handle electrical emergencies.