“Copper or plastic? That is the question.” As you embark on your plumbing journey, this question may arise, leaving you to ponder the best choice for your home.
In this article, we will explore the world of copper pipes, their benefits and drawbacks, and how they stack up against other materials. So, let’s dive in and discover if copper is the right choice for your plumbing needs.
Is plumbing made of copper?
Plumbing systems can be made of various materials, and one commonly used material is copper.
Copper plumbing has been widely utilized for its durability, corrosion resistance, and ability to handle high water pressure.
Its malleability allows for easy installation, and copper pipes are often soldered or connected using compression fittings.
Also, copper has antimicrobial properties, making it a hygienic choice for carrying water.
However, it’s worth noting that other materials such as PVC (polyvinyl chloride) and PEX (cross-linked polyethylene) have gained popularity in recent years due to their affordability and ease of installation, offering alternatives to traditional copper plumbing.
What are the benefits of using copper pipes for plumbing?
- Durability: Copper pipes are known for their long lifespan. They are resistant to corrosion and can withstand extreme temperatures, making them highly durable and reliable for plumbing systems.
- Excellent heat conduction: Copper is an excellent conductor of heat, making it ideal for hot water systems. It allows for quick and efficient heat transfer, ensuring hot water reaches the desired destination promptly.
- Resistance to bacterial growth: Copper has natural antimicrobial properties that help inhibit the growth of bacteria, viruses, and fungi. This feature makes copper pipes a hygienic choice for carrying drinking water and reduces the risk of contamination.
- Safety: Copper is a non-combustible material, which means it does not burn or contribute to the spread of fires. This fire-resistant characteristic makes copper pipes a safer option for plumbing systems, especially in residential and commercial buildings.
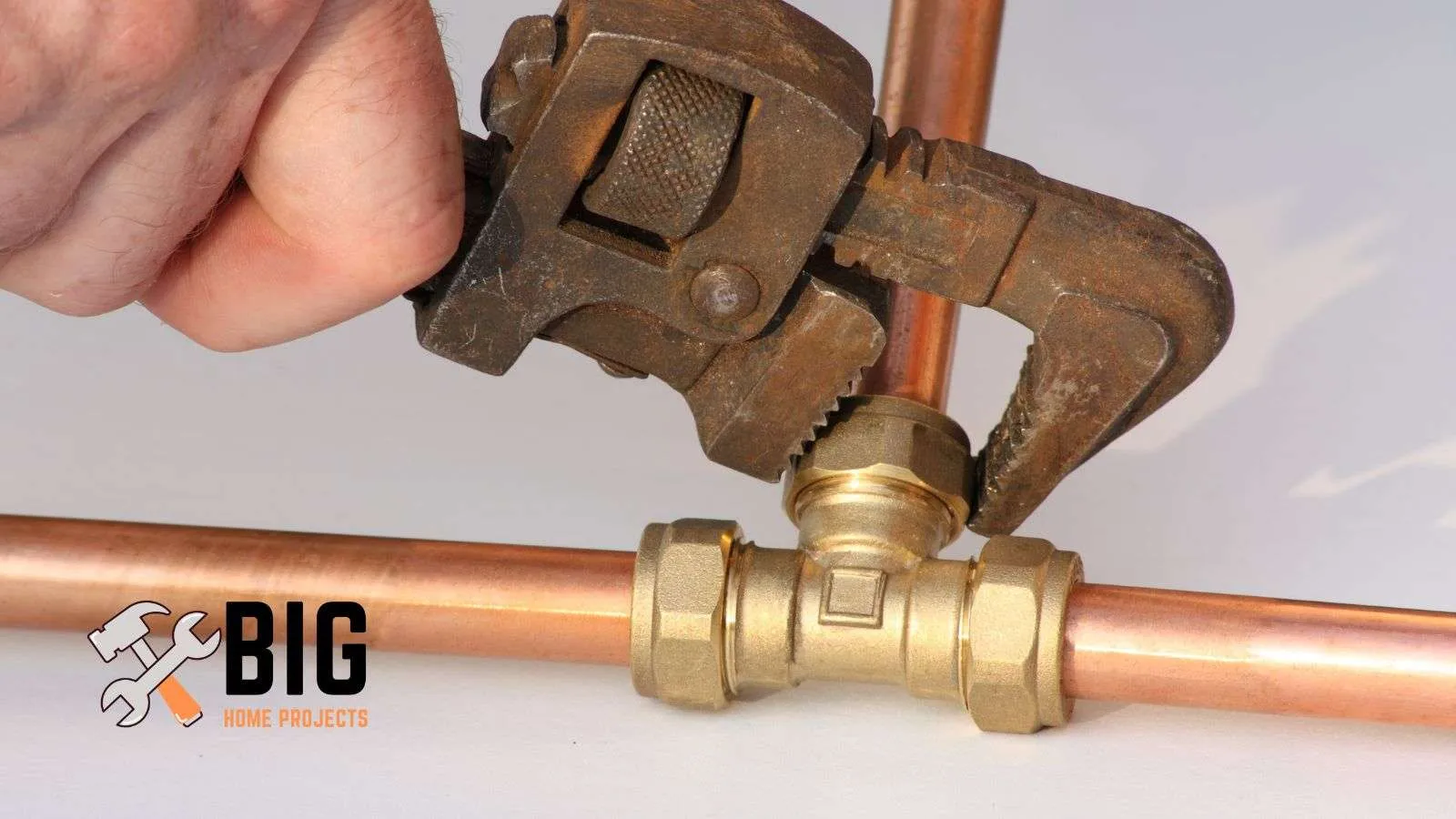
- Easy installation: Copper pipes are malleable and can be easily bent and shaped, allowing for straightforward installation. They can be soldered or connected using compression fittings, providing flexibility during the plumbing process.
- Compatibility: Copper pipes are compatible with a wide range of plumbing systems and fittings. They can be integrated with existing plumbing infrastructure or combined with other materials if needed.
- Resistant to UV rays: Unlike some plastic piping materials, copper pipes are not affected by exposure to UV rays. This makes them suitable for both indoor and outdoor plumbing applications.
What are the drawbacks of using copper pipes for plumbing?
- Cost: Copper pipes tend to be 3 to 4 times more expensive compared to other materials such as PVC or PEX. The higher cost of copper can make it a less attractive option, especially for large-scale plumbing projects or budget-conscious individuals.
- Prone to corrosion in certain conditions: Although copper is generally resistant to corrosion, it can be susceptible to corrosion in certain circumstances. High levels of acidity or alkalinity in the water, as well as aggressive soil conditions, can lead to the degradation of copper pipes over time.
- Vulnerability to freezing: Copper pipes can be susceptible to freezing and subsequent bursting if they are exposed to extremely cold temperatures. In regions with harsh winters, proper insulation or other preventative measures may be necessary to protect copper pipes from damage.
- Conductivity: While the excellent heat conductivity of copper pipes is an advantage for hot water systems, it can also be a disadvantage. Copper pipes can potentially cause heat loss if they run through cold spaces, requiring additional insulation to mitigate this effect.
- Susceptibility to theft: Unfortunately, due to its scrap value, copper pipes can be a target for theft. This is particularly relevant in vacant or unattended properties, where the removal of copper pipes can result in costly repairs and inconvenience.
- Noise transmission: Copper pipes can transmit noise more effectively compared to some other plumbing materials. Water flow or pressure fluctuations within copper pipes can create water hammer or other audible sounds, which may be a concern in certain residential or commercial settings.
- Environmental impact: The extraction and production of copper can have environmental consequences. Mining copper ore and the energy-intensive processes involved in refining and manufacturing copper pipes contribute to carbon emissions and resource consumption.
How long does copper piping last?
Copper piping is renowned for its durability and can last for several decades when properly installed and maintained.
On average, copper pipes have an expected lifespan of 50 to 70 years or longer.
Factors that can influence their longevity include water quality, installation quality, maintenance, environmental conditions, and water usage patterns.
Highly acidic or alkaline water, poor installation practices, a lack of maintenance, aggressive soil conditions, extreme temperatures, and excessive water pressure can all impact the lifespan of copper pipes.
However, with regular inspections, prompt repairs, and appropriate care, copper pipes can provide reliable plumbing for many years.
What are the different types of copper pipes available?
| Copper Pipe Type | Pros | Cons |
| Type M | Lower cost compared to other types. Suitable for low to moderate water pressure. Easy to work with and install. | Thinner walls, which may be more susceptible to damage or bursting. Not recommended for high-pressure applications. Limited use in commercial or industrial settings. |
| Type L | Versatile for both residential and commercial applications. Thicker walls provide increased durability. Can handle higher water pressure. Commonly used for hot water distribution. | Higher cost compared to Type M. Limited use in extremely high-pressure applications. Thicker walls may reduce water flow rates in some cases. |
| Type K | Thickest walls for maximum durability and high-pressure applications. Suitable for underground water mains and industrial use. | Highest cost among the copper pipe types. Thicker walls may restrict water flow in certain situations. Limited use in residential applications due to excessive thickness. |
This table provides a comparison of different types of copper pipes, outlining their respective advantages and disadvantages based on factors such as cost, water pressure suitability, durability, and application limitations.
- Type M: Type M copper pipes have the thinnest walls and are typically used for residential applications with low to moderate water pressure. They are commonly used for plumbing fixtures such as sinks, toilets, and bathtubs.
- Type L: Type L copper pipes have thicker walls compared to Type M and are suitable for both residential and commercial applications. They can handle higher water pressure and are commonly used for water supply lines, hot water distribution, and outdoor plumbing.
- Type K: Type K copper pipes have the thickest walls and are typically used in commercial and industrial applications where high water pressure is expected. They are commonly used for underground water mains, industrial processes, and heavy-duty applications.
Is copper piping safe for use with drinking water?
Copper piping is generally considered safe for use with drinking water.
Copper has natural antimicrobial properties that inhibit the growth of bacteria, viruses, and fungi, helping to maintain water quality.
Copper pipes do not leach harmful chemicals into the water, ensuring that it remains free from contamination.
However, it’s important to note that in certain circumstances, such as high levels of acidity or alkalinity in the water or when the water sits stagnant for extended periods, copper pipes may contribute to a slight metallic taste.
Regular water testing and proper maintenance of copper pipes can help ensure the safety and quality of drinking water in plumbing systems.
How do you install copper pipes in a plumbing system?
- Planning and preparation: Determine the layout and design of the plumbing system, including the desired locations for water supply lines and fixtures. Take accurate measurements and make a materials list to ensure you have the necessary copper pipes, fittings, and other components.
- Shut off the water: Before starting any installation work, ensure that the water supply to the area is turned off. This prevents water flow and allows for a safe and dry working environment.
- Cut the copper pipes: Use a pipe cutter or a hacksaw to cut the copper pipes to the required lengths. Ensure clean, burr-free cuts for proper fitting connections.
- Clean and deburr the ends: After cutting the pipes, use a deburring tool or sandpaper to remove any rough edges or burrs from the cut ends. Clean the ends thoroughly to remove any dirt, grease, or debris.
- Dry-fit and mark: Dry-fit the pipes and fittings together without using any adhesive or solder. This helps ensure accurate alignment and allows for any necessary adjustments. Mark the pipe lengths and fitting positions for reference during the soldering process.
- Apply flux: Apply a thin, even layer of flux to the outside of the pipe ends and the inside of the fittings. Flux helps promote proper solder adhesion and creates a watertight seal.
- Soldering: Use a propane torch or a soldering iron to heat the joint where the pipe and fitting meet. Once the joint reaches the appropriate temperature, touch the solder wire to the joint, allowing it to flow and create a strong bond. Ensure proper solder penetration around the entire joint. Repeat the process for all necessary connections.
- Pressure test and inspection: After completing the soldering, conduct a pressure test to ensure there are no leaks in the system. Close all fittings and valves, then pressurize the system using air or water. Check for any leaks or pressure drops and make necessary adjustments or repairs.
- Secure the pipes: Use appropriate pipe hangers, clips, or straps to secure the copper pipes in place, ensuring they are properly supported and aligned. This prevents unnecessary movement or stress on the pipes.
- Connect to fixtures: Install shut-off valves, faucets, and other fixtures as required, connecting them to the copper pipes using appropriate fittings and connectors.
How do you repair plumbing pipes made of copper?
- Identify the leak: Locate the area of the copper pipe where the leak or damage is occurring. It may be a visible hole, a joint, or a crack.
- Shut off the water: Before beginning any repair work, turn off the water supply to the affected area. This prevents further water damage and allows for a dry working environment.
- Drain the water: Open faucets and drain any remaining water from the plumbing system to minimize the water flow and pressure within the pipes.
- Cut out the damaged section: Using a pipe cutter, cut out the damaged section of the copper pipe. Make clean, straight cuts on either side of the damaged area. Ensure the ends are smooth and free from burrs.
- Measure and cut a replacement pipe: Measure the gap left by the removed section and cut a new piece of copper pipe to the required length. Use the appropriate pipe cutter or hacksaw for a precise cut.
- Prepare the pipe ends: Clean the cut ends of the existing pipe and the replacement pipe. Use a deburring tool or sandpaper to remove any burrs or rough edges. Ensure the surfaces are clean and free from dirt or debris.
- Connect the replacement pipe: Apply flux to the cleaned pipe ends and the inside of the appropriate fittings. Insert one end of the replacement pipe into one fitting, and the other end into the remaining fitting, ensuring a proper fit and alignment.
- Solder the joints: Use a propane torch or a soldering iron to heat the joint where the pipe and fitting meet. Apply solder to the joint, allowing it to flow and create a strong bond. Ensure complete solder penetration around the entire joint. Repeat the process for all necessary connections.
- Allow the pipe to cool: Allow the soldered joints to cool down naturally. Do not disturb or manipulate the pipe until it has fully cooled.
- Pressure test and inspect: Once the repair is completed, conduct a pressure test to check for any leaks. Close all valves and fittings, then pressurize the system using air or water. Inspect the repaired area for any signs of leakage or pressure drops. Make any necessary adjustments or repairs if required.
What is the best way to prevent the corrosion of copper pipes?
To prevent the corrosion of copper pipes, it is important to maintain proper water chemistry by avoiding highly acidic or alkaline water and conducting regular water testing.
Controlling water velocity through the use of pressure regulators or flow restrictors helps prevent turbulence and erosion.
Adequate pipe insulation in cold areas prevents condensation and freezing. Dielectric unions should be used when connecting copper pipes to dissimilar metals, while sacrificial anodes can divert corrosion away from copper pipes.
Proper grounding and regular maintenance and inspection are essential to identifying and addressing corrosion issues promptly.
Professional plumbing installation techniques, including proper soldering and support, help minimize the risk of corrosion.
Are copper pipes susceptible to freezing?
Copper pipes can be susceptible to freezing under certain conditions. Copper itself is not as vulnerable to freezing as some other materials, such as plastic pipes, but it can still be affected.
When water inside copper pipes freezes, it expands and can potentially cause the pipes to crack or burst.
However, the risk of freezing depends on several factors, including the temperature, duration of exposure, insulation, and water flow.
Copper pipes in unheated areas, such as crawl spaces, attics, or exterior walls, are more prone to freezing.
To prevent freezing, it is important to properly insulate and protect these pipes.
Insulation materials like foam sleeves or pipe wraps can be used to provide an extra layer of protection.
Also, during extremely cold weather, allowing a slow trickle of water to flow through the pipes can help prevent freezing by keeping the water in motion.
What are the different fittings used with copper pipes?
- Coupling: Couplings are used to connect two copper pipes together in a straight line.
- Elbow: Elbows have a 90-degree or 45-degree bend and are used to change the direction of a copper pipe. They are available in different angles to suit specific plumbing needs.
- Tee: Tees have a T-shaped design and are used to create a branch connection in a copper pipe system, allowing for the addition of a new line.
- Cross: Cross fittings have a plus (+) shape and are used to create a four-way connection in copper pipe systems.
- Reducer: Reducers are used when transitioning from one pipe size to a smaller size or vice versa. They help accommodate changes in pipe diameter.
- Union: Unions are used to provide a detachable joint in a copper pipe system. They allow for easy disassembly and reassembly of pipes, making maintenance or repairs more convenient.
- Cap: Caps are used to seal the end of a copper pipe, preventing the flow of water. They are often used temporarily during construction or when a section of the pipe needs to be closed off.
- Valve: Valves are used to control the flow of water within a copper pipe system. They can be used to shut off or regulate the water supply to specific areas or fixtures.
- Compression fitting: Compression fittings use a nut and sleeve to create a tight seal between the copper pipe and the fitting. They are commonly used for connections to fixtures, such as faucets or toilets.
- Soldered/sweat fitting: Soldered or sweat fittings are used in conjunction with soldering techniques to create a strong, permanent connection between copper pipes. They require heating the joint and applying solder to create a secure bond.
What’s the difference between copper pipes and plastic pipes?
Copper pipes are made of solid copper, a durable metal known for its corrosion resistance and longevity.
Copper has been used in plumbing for many years due to its reliability and performance.
Copper pipes are commonly used for both hot and cold water supply lines, as well as for heating systems.
They are suitable for a wide range of applications in residential, commercial, and industrial plumbing.
However, installing copper pipes involves cutting the pipes to the required lengths, soldering or brazing the fittings, and creating watertight connections.
It requires specialized tools and skills, often necessitating the expertise of a professional plumber.
Copper pipes are generally more expensive than plastic pipes, both in terms of material cost and installation labor.
On the other hand, plastic pipes are made of synthetic materials like PVC or PEX.
These materials offer different characteristics and properties compared to copper.
Plastic pipes are relatively easier to install due to their lightweight and flexible nature.
They can be cut with simple tools and connected using solvent cement (for PVC) or compression fittings (for PEX).
The simpler installation process makes plastic pipes more suitable for DIY projects.
Plastic pipes, especially PVC, are commonly used for drainage and wastewater systems, while PEX pipes are often used for water supply lines.
Plastic pipes are generally more affordable than copper pipes, making them a cost-effective option for plumbing projects.
In terms of durability, copper pipes are known for their longevity and resistance to high temperatures, UV rays, and corrosion.
They can withstand various water conditions and physical stress. However, improper installation or certain water conditions can lead to corrosion issues in copper pipes.
Plastic pipes are also durable and resistant to corrosion and scale buildup.
They are less prone to damage from freezing temperatures and can withstand chemical exposure.
However, plastic pipes may be susceptible to UV degradation over time, and their long-term durability can vary depending on the specific type of plastic material used.
What tools do you need to cut copper pipes
- Pipe cutter: A pipe cutter is specifically designed to cut copper pipes. It consists of a sharp cutting wheel that rotates around the pipe, gradually scoring and cutting through the copper.
- Deburring tool: After cutting the copper pipe, a deburring tool is used to remove any sharp edges or burrs created during the cutting process. This ensures a smooth and clean edge for proper fitting connections.
- Hacksaw: In situations where a pipe cutter is not available or suitable, a hacksaw can be used to cut copper pipes. It requires more effort and caution to achieve a clean cut.
- Tube cutter: For smaller diameter copper pipes, a tube cutter can be used. This handheld tool is similar to a pipe cutter but is specifically designed for pipes with diameters around 1 inch or smaller.
What is copper leaching and should I be worried?
Copper leaching refers to the process where copper particles or ions are released into the water supply.
This can occur when the water comes into contact with copper pipes, fittings, or fixtures.
Copper leaching is generally not a significant concern for drinking water safety.
Copper is an essential nutrient that the body needs in small amounts, and the levels of copper typically found in water from copper plumbing systems are unlikely to pose health risks.
In certain situations, such as homes with acidic water or when excessive amounts of copper are present, it may be advisable to test the water and take appropriate measures to address any potential concerns.
Is copper used in new or older homes?
Copper has been used in both new and older homes for plumbing systems.
In older homes, copper pipes were commonly installed as the primary material for plumbing.
In recent years, plastic pipes like PVC and PEX have gained popularity due to their ease of installation and affordability.
Copper is still widely used in new homes, especially for specific applications such as water supply lines, heating systems, or in areas where local plumbing codes require its use.
How much is copper plumbing cost?
Copper plumbing costs between $4 and $12 per linear foot on average. This doesn’t include removal of the existing supply lines.
The cost to re-pipe a house with copper pipe is $8,000 to $16,000 or $3 to $8 per linear foot. Replacing galvanized drain, waste, and vent pipe with copper costs $13 to $15 per linear foot.
Other interesting articles: